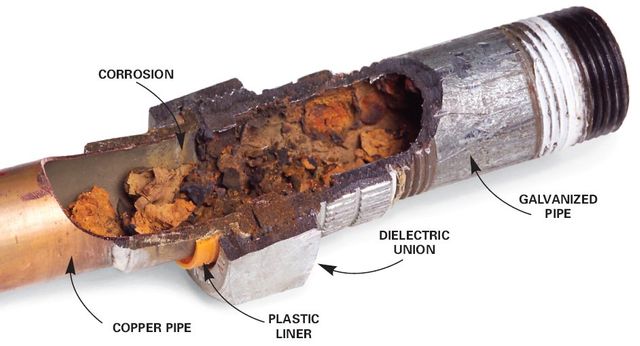
How Are Pipes Galvanised?
Pipes galvanisation is a process that is used to protect metal from corrosion. It is a procedure that involves coating the surface of the metal with a layer of zinc. This layer is then bonded to the metal to form a protective barrier against corrosion. This process is used for a variety of different metals and pipes, and is especially beneficial when used on steel and iron pipes. Galvanisation is often used in the construction and plumbing industries, as it is an economical and efficient way to protect pipes from corrosion.
What Is Galvanisation?
Galvanisation is a process of coating steel or iron with a zinc layer in order to protect it from corrosion. It is a widely used technique in the construction and production of pipes, as it helps to prevent the formation of rust and other corrosion-related issues. Galvanisation is achieved by submerging the pipes in a bath of molten zinc, which then forms a protective layer around them. This layer is then sealed by a chemical or physical process. The end result is a highly durable and long-lasting pipe which can withstand the elements and maintain its integrity for years. Galvanisation is an effective and economical way to extend the life of pipes and keep them in good condition.
Types of Galvanisation
Pipes are a vital component of many complex industrial and household systems. To ensure the longevity and quality of pipes, manufacturers often employ a process called galvanisation. This process is used to protect metal surfaces from corrosion and rust by coating them with a layer of zinc. But how exactly does galvanisation work? And what are the different types of galvanisation?
Galvanisation is primarily used to protect metal surfaces from corrosion and rust. The process involves the application of a zinc coating to the surface of the metal. This zinc coating acts as a barrier between the metal surface and the environment, preventing the metal from coming into contact with water, air, and other elements that could cause it to corrode or rust.
There are two main types of galvanisation: hot-dip galvanisation and electro-galvanisation. Hot-dip galvanisation is the preferred method of galvanisation since it provides the most durable protection against corrosion and rust. This method involves dipping the metal surface into a bath of molten zinc. The zinc coating forms a strong bond with the metal, providing a long-lasting layer of protection. Electro-galvanisation, on the other hand, is a less durable form of galvanisation. This method involves coating the metal surface with a zinc coating using electrical current.
Galvanisation is a reliable process that can help protect metal surfaces from corrosion and rust. It is important to understand the different types of galvanisation and the benefits they provide so that you can make the best decision for your needs.
Advantages of Galvanising Pipes
Galvanising pipes is a process of coating iron or steel pipes with a protective layer of zinc. This process helps to protect the metal from corrosion and wear, making it more durable and helping to extend its lifespan. Galvanised pipes are used in various applications, from plumbing to structural support. But what are the advantages of galvanising pipes?
Firstly, galvanising pipes can help to reduce the risk of corrosion. The zinc coating prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the metal, which would otherwise cause oxidation and rust. This coating also helps to prevent the build-up of debris, such as rust and dirt, which can further contribute to corrosion.
Secondly, galvanised pipes are incredibly durable and can last for many years in outdoor and extreme environments. The zinc coating helps to protect the metal from wear and tear, making it less susceptible to damage. Galvanised pipes can also be painted, which can help to protect them from the elements and further extend their lifespan.
Finally, galvanised pipes are relatively inexpensive. As they are already coated with zinc, there is no need to purchase additional protective coatings, which can be expensive. This makes galvanised pipes an affordable option for a variety of applications.
In conclusion, galvanising pipes offers a number of advantages. It helps to prevent corrosion, increases their durability, and helps to keep costs down. As such, it is an ideal choice for a variety of applications.

Process of Galvanising Pipes
Galvanisation is a process used to protect metal from corrosion. This process is commonly used to coat steel pipes, as it protects them from rust and other forms of damage. The galvanisation process involves coating a metal surface with a thin layer of zinc, which prevents the metal from corroding. The process of galvanising pipes involves a number of steps, including pre-treatment, dipping in a bath of molten zinc, and post-treatment.
The pre-treatment process involves cleaning the pipes to ensure they are free of dirt, grease, and other contaminants. The pipes are then dipped in a bath of molten zinc at about 450°C. The zinc adheres to the surface and forms a protective layer that prevents the pipe from corroding. After the pipes are removed from the bath, they are passed through a cooling chamber before being post-treated. The post-treatment process involves the application of a sealant to the pipes to ensure the zinc coating remains intact.
Galvanising pipes is an effective way to prevent corrosion and prolong the life of the pipes. The galvanising process can be done quickly and efficiently, and is cost-effective compared to other methods. The protective coating is also more durable than paint and other coatings, making it an ideal solution for pipes that come into contact with water or other liquids.
Key Considerations for Galvanising Pipes
Pipes are often galvanised for corrosion protection, as galvanising provides a protective layer that prevents oxidation and other forms of corrosion. Galvanising involves applying a zinc coating to the metal surface, which prevents rust and other forms of corrosion. Understanding the process, as well as the various considerations involved when galvanising pipes, is crucial to achieving a successful result.
The first step for galvanising pipes is to clean the surface. This is done to remove any dirt, debris, or other contaminants that could interfere with the galvanising process. This is a critical step and should not be overlooked. The pipes should be thoroughly cleaned and dried before proceeding with the galvanising process.
The next step is to prepare the pipes for galvanising. This involves sandblasting the surface of the pipes to remove any existing corrosion and to create a smooth, even surface for the zinc coating. Once the surface is ready, the pipes can then be heated and dipped into a hot zinc bath. The bath must be hot enough to properly adhere the zinc coating to the pipes.
Finally, once the pipes are galvanised, they must be inspected for any defects. Any defects must be addressed before the pipes can be used. It is important to note that galvanised pipes can be brittle and require additional structural support when used in certain applications.
Galvanising pipes is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail and consideration of various factors. Cleaning, preparing, and inspecting the pipes are all essential steps to ensure a successful result. By following these steps and understanding the process, it is possible to ensure that the pipes are properly galvanised and protected from corrosion.
Best Practices for Galvanising Pipes
Galvanising pipes is a process that helps protect them from corrosion and rust. It involves coating the pipes with a layer of zinc, which is a highly reactive metal that forms a protective layer on the surface of the material. Galvanising has been used for years in the construction industry and is often the preferred method for protecting pipes from the elements. However, there are certain best practices that should be followed when galvanising pipes, which include proper preparation of the surface, the use of an appropriate flux, and the use of the correct galvanising temperature. Proper preparation of the surface involves cleaning the pipe of any dirt or debris, as this can prevent the zinc from properly adhering to the pipe. The use of an appropriate flux can help protect the zinc from oxidation and ensure that the coating is of the highest quality. Finally, the correct galvanising temperature is also important, as it can help ensure that the zinc adheres properly to the material. By following these best practices, the galvanised pipes should last for many years and provide the desired protection from corrosion and rust.
FAQs About the How Are Pipes Galvanised?
Q1. What is galvanisation?
A1. Galvanisation is a process of coating steel or iron with a protective layer of zinc in order to prevent corrosion and rust.
Q2. What is the benefit of galvanised pipes?
A2. Galvanised pipes are more resistant to corrosion and rust, which makes them a more durable and cost-effective choice for plumbing and other applications.
Q3. How long do galvanised pipes last?
A3. The longevity of galvanised pipes depends on several factors, such as the environment, water quality, and the thickness of the zinc layer. Generally, galvanised pipes can last for years or even decades if maintained properly.
Conclusion
Galvanising pipes is a great way to protect them from corrosion and extend their life. The process involves coating pipes in a layer of zinc which is an effective barrier against corrosion and other environmental factors. This process can also be used on other metal items to protect them from corrosion. Galvanised pipes can last for many years and are a great choice for outdoor use, especially in areas with high humidity and other environmental conditions that could cause corrosion.