How Does A Toilet Work?
A toilet is one of the most essential fixtures of a modern home, and although its use and design may vary, the basic principles of how it works remain the same. In general, toilets use water and gravity to flush waste away from the bowl and down the drain. Toilets are made up of two main parts: a tank and a bowl. The tank is located behind the bowl and contains two valves: a flush valve and a refill valve. When the flush valve is triggered, the water stored in the tank is released into the bowl, creating a strong downward force that helps to flush the waste away. After the flush is complete, the refill valve begins to fill the tank with fresh water, and the bowl is refilled with water as well.
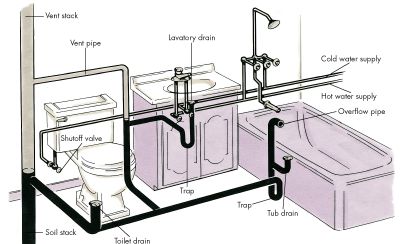
Anatomy of a Toilet
Toilets are more complex than most people understand. The inner workings of a toilet are a fascinating combination of mechanics, plumbing, and chemistry. To understand how a toilet works, it is essential to know the anatomy of a toilet.
At the heart of a toilet is a tank that stores the water used to flush the toilet. The tank is connected to a water supply pipe and a flush valve, which controls the amount of water that enters the tank. On the side of the tank is the fill valve, which regulates the water level in the tank. When the flush handle is pressed, the flush valve opens, sending the water in the tank rushing into the bowl.
The bowl is designed to use the rushing water to create a siphon. The water swirls around the bowl, carrying the waste down into the drainpipe. The bowl has a trapway, which is a curved pipe that helps to prevent odors from the sewer from entering the bathroom.
The water also passes through a shutoff valve, which stops the flow of water when the toilet is flushed. When the flush handle is released, the flush valve closes and the fill valve opens, sending more water into the tank to refill it.
Understanding the anatomy of a toilet can help you troubleshoot common toilet problems. Knowing how a toilet works can also help you conserve water and keep your toilet running efficiently for years to come.
Types of Toilets
Toilets come in various shapes and sizes, and they all work differently depending on their design. The two most common types of toilets are gravity-flush toilets and pressure-assisted toilets. Gravity-flush toilets use gravity to help flush waste away. This type of toilet is the most common in the United States and can be found in most households. Pressure-assisted toilets, on the other hand, use pressurized air to help flush waste away. This type of toilet is usually found in commercial buildings and is known for its powerful flush and low water usage. Both types of toilets are designed to help remove waste from the bowl and send it down the drain. Understanding the difference between the two types of toilets can help you make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the right one for your home.
How a Toilet is Filled
Toilets are essential fixtures in our homes and businesses, but how exactly do they work? Many people know that toilets flush and fill with water, but few understand the intricate mechanics behind this process. Toilet fill and flush cycles are complex, but understanding how they work can help you identify and repair potential issues.
The key components of a toilet’s fill and flush cycle are the water inlet valve, the flush valve, the trapway, and the water outlet valve. When the toilet is flushed, the flush valve opens, allowing water to flow into the trapway. The trapway, which is a curved piece of pipe, stores the water until it reaches the water outlet valve at the bottom. The water outlet valve, which is also known as the flush valve, opens, allowing the water to flow into the bowl and down the drain.
To refill the tank, the inlet valve opens and water flows from the incoming water supply line. When the water reaches a certain level, the float valve opens and closes, allowing water into the tank until it reaches the desired level. The fill cycle is complete when the water inlet valve closes again.
Understanding how a toilet is filled and emptied is the first step toward solving potential problems. With a basic understanding of toilet mechanics, you can identify and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
How a Toilet is Flushed
Toilets are a vital piece of plumbing that are used in almost every home. But how exactly does a toilet work? To understand how a toilet works, it’s important to understand the flushing process. A toilet is designed to flush waste away from the user’s home, and the process of flushing is powered by water. To flush a toilet, a user pushes down on the flush handle, which is connected to a system of valves, tanks, and pipes. The flush handle opens the flush valve, which allows the tank of water to quickly enter the toilet bowl. This water pressure forces the waste out of the bowl and into the drain. The water continues to fill the bowl until the flush valve closes, and the tank begins to refill. To complete the flush cycle, a user releases the handle, which returns the flush valve to its closed position and starts the refill cycle. This process repeats each time the toilet is flushed, and the amount of water used can be adjusted to suit the user’s needs. With proper maintenance, a toilet can be a reliable and efficient way to dispose of waste.
Common Problems with Toilets
Toilet technology has come a long way, but that doesn’t mean they’re always reliable. Unfortunately, common problems with toilets are an inevitable part of owning one. From clogs and leaks to running toilets and poor flushing, these issues can be both annoying and expensive to repair. Understanding the common problems with toilets and how to identify potential issues can help you save time and money in the long run.
Clogs are one of the most common problems with toilets and are often caused by foreign objects that are flushed down the toilet. If the clog is small enough, it can typically be cleared with a plunger. However, if the clog is too large, a professional plumber may be necessary to unclog the toilet.
Leaks are another common issue and can range from a slow leak to a full-blown flood. These leaks can be caused by faulty seals or loose connections in the toilet or plumbing system. If the leak is minor, it can be repaired by tightening the connections. However, if the leak is more severe, you may need to replace the affected parts.
Running toilets are another issue and are typically caused by a faulty flapper or fill valve. If the flapper is worn out or won’t shut properly, the toilet will continue to run. Replacing the flapper can usually solve the issue.
Finally, poor flushing is a common problem and can be caused by clogs, low water pressure, or a faulty flapper. If the clog is too large to clear with a plunger, a professional plumber may be needed to unclog it. If the water pressure is too low, you may need to adjust the pressure. Finally, if the flapper is worn out, it may need to be replaced.
By understanding the common problems with toilets and how to identify potential issues, you can save time and money in the long run. If you’re experiencing any of these issues, it’s best to contact a professional plumber as soon as possible to ensure your toilet is running efficiently.
Maintenance Tips for Toilets
Toilets are an important part of our everyday lives and proper maintenance is essential for keeping them in good working order. With a little bit of know-how and regular maintenance, your toilet can provide years of reliable service. Here are some essential tips for keeping your toilet in good condition.
First, always check for any signs of leaks. A leaking toilet can waste a significant amount of water, so it’s important to identify and repair any leaks as soon as possible. Additionally, regularly inspect the toilet’s flapper and fill valve to ensure they’re functioning properly. If you suspect any problems, it’s best to call a plumber for assistance.
Second, try to clean the toilet bowl regularly. A good scrubbing with a brush and cleaner can help remove soap scum and other buildup, and can also help prevent stains from forming. Additionally, use a toilet bowl cleaner to help keep the bowl clean and fresh.
Finally, be sure to check the toilet for any signs of damage. If you notice any cracks or loose bolts, it’s important to call a plumber for help. Additionally, if the toilet is clogged or running slowly, try using a plunger or drain snake to clear the blockage.
By following these simple maintenance tips, you can help keep your toilet in good working order for years to come. Regular maintenance and inspection can go a long way in ensuring your toilet remains functioning properly.
FAQs About the How Does A Toilet Work?
1. What is the function of the float valve in a toilet?
A float valve is a component of a toilet that allows water to move from the tank to the bowl to refill the bowl after flushing. It is typically a plastic or metal ball attached to a rod which is connected to a valve.
2. What is the difference between a gravity flush toilet and a pressure-assisted toilet?
A gravity flush toilet uses gravity to move the water from the tank to the bowl. A pressure-assisted toilet uses compressed air to rapidly move the water from the tank to the bowl.
3. How often should I replace the fill valve in my toilet?
It is recommended that the fill valve be replaced every 5-7 years. This is because the valve can become corroded over time which can lead to leaks and other issues.
Conclusion
A toilet is a complex and important plumbing fixture that is essential for modern living. Toilets use gravity and water pressure to flush waste away from your home and into the sewer system. Water is stored in the tank, and when the flush lever is activated, the flapper valve opens and allows the water to rush into the bowl and create a powerful vacuum that sucks the waste away. This process is repeated each time the toilet is flushed, ensuring that waste is removed from the home quickly and efficiently.