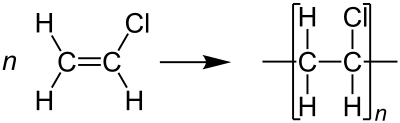
What are the 4 types of PVC?
PVC, which stands for polyvinyl chloride, is a versatile material used in various applications, from construction and manufacturing to healthcare and packaging. But did you know that there are different types of PVC available? In this article, we will explore the four main types of PVC and their specific characteristics.

Types of PVC:
- Rigid PVC: Rigid PVC, also known as unplasticized PVC (uPVC), is a type of PVC that is characterized by its rigidity and strength. This type of PVC is commonly used in building and construction projects due to its resistance to corrosion and weathering. Unlike other types of PVC, rigid PVC does not contain any plasticizers, making it more durable and less prone to deformation. It is often used in applications where strength and structural integrity are crucial, such as window frames, pipes, and outdoor signage. Rigid PVC is known for its excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for use in environments that involve exposure to harsh chemicals. Additionally, it has good electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for electrical conduit systems. The rigidity of uPVC also allows for easy installation and maintenance, as it can be easily cut and shaped to fit specific requirements.
- Flexible PVC, also known as plasticized PVC (pPVC), is a type of PVC that offers enhanced flexibility and elasticity. This type of PVC contains plasticizers, which are added to the PVC resin during the manufacturing process to increase its flexibility. The plasticizers make the PVC more pliable and easier to manipulate, allowing it to be used in a wide range of applications. Flexible PVC is commonly used in products that require a softer and more bendable material, such as cables, hoses, inflatable toys, and medical devices. Its flexibility allows for easy handling and installation, making it a popular choice in industries where ease of use and adaptability are important. Additionally, flexible PVC is resistant to chemicals, making it suitable for applications that involve exposure to various substances.
- Chlorinated PVC (CPVC): Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) is a type of PVC that has been chemically modified by adding chlorine to the polymer structure. This modification enhances the heat and flame resistance of the PVC, making CPVC suitable for applications that involve high temperatures. CPVC is commonly used in plumbing systems, as it can withstand higher water temperatures compared to standard PVC. In addition to its heat resistance, CPVC also offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for use in aggressive environments. It is often used in fire sprinkler systems, where its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion is crucial. CPVC pipes are also commonly used in hot water supply systems, where the higher operating temperatures necessitate a more heat-resistant material.
- Foam PVC: Foam PVC, also known as expanded PVC, is a type of PVC that has been expanded to create a lightweight and versatile material. This type of PVC is characterized by its low density and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Foam PVC is often used in the signage industry, where its lightweight nature allows for easy installation and transportation. Foam PVC has good insulation properties, both thermal and electrical, making it suitable for applications that require these properties. It is also resistant to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Foam PVC is commonly used in advertising signs, display boards, and exhibition stands, where its lightweight and durable nature make it a preferred choice.
- Applications of rigid PVC: Rigid PVC, or uPVC, finds wide applications in various industries. One of the most common applications of rigid PVC is in the construction industry, where it is used for window frames, doors, and pipes. The rigidity and strength of uPVC make it an excellent choice for these applications, as it can withstand the harsh outdoor conditions and provide long-lasting performance. Another common use of rigid PVC is in the electrical industry, where it is used for electrical conduit systems. The excellent electrical insulation properties of uPVC make it a preferred choice for protecting electrical wires and cables. Additionally, rigid PVC is used in the manufacturing of vinyl records, credit cards, and automotive components.
- Applications of flexible PVC: Flexible PVC, or PVC, has a wide range of applications due to its flexibility and ease of use. One of the main applications of flexible PVC is in the production of cables and wires. The flexibility of PVC allows for easy bending and routing of cables, making it an ideal choice for applications that require flexibility and durability. In addition to cables, flexible PVC is used in the manufacturing of inflatable toys and medical devices. The soft and pliable nature of PVC makes it suitable for applications that require a comfortable and safe material. It is also commonly used in the production of flexible hoses, tubing, and gaskets, where its flexibility allows for easy installation and maintenance.
- Applications of CPVC: CPVC, or chlorinated PVC, is primarily used in plumbing systems and fire sprinkler systems. The enhanced heat and flame resistance of CPVC make it suitable for applications that involve high temperatures, such as hot water supply systems and fire protection systems. CPVC pipes are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings, where the higher water temperatures require a more heat-resistant material. In addition to plumbing systems, CPVC is also used in industrial applications that involve aggressive chemicals and corrosive environments. Its excellent corrosion resistance and chemical resistance make it a preferred choice for applications that require long-term durability and performance. CPVC is commonly used in chemical processing plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and industrial piping systems.
- Applications of foam PVC: Foam PVC, or expanded PVC, has a wide range of applications due to its lightweight and versatile nature. One of the main applications of foam PVC is in the signage industry, where it is used for advertising signs, display boards, and exhibition stands. The lightweight nature of foam PVC allows for easy installation and transportation, making it a preferred choice in the signage industry. Foam PVC is also used in the construction industry for applications such as decorative trim, molding, and decorative panels. The lightweight nature of foam PVC makes it easy to handle and install, while its durability ensures long-lasting performance. Additionally, foam PVC is used in the manufacturing of packaging materials, foam sheets, and insulation boards.
Comparison of the 4 types of PVC:
When comparing the four types of PVC, it is important to consider their specific characteristics and applications. Rigid PVC, or uPVC, is known for its rigidity and strength, making it suitable for building and construction projects. Flexible PVC, or pPVC, offers enhanced flexibility and is commonly used in applications that require a soft and pliable material.Chlorinated PVC, or CPVC, offers improved heat and flame resistance compared to standard PVC, making it suitable for plumbing and fire protection systems. Foam PVC, or expanded PVC, is a lightweight and versatile material that finds applications in the signage industry and construction industry.Each type of PVC has its own unique properties and applications, and it is important to choose the right type of PVC for your specific project or application. Consider factors such as the required level of rigidity or flexibility, the operating temperatures, and the exposure to chemicals or harsh environments. By understanding the characteristics of each type of PVC, you can make an informed decision and ensure the best performance and durability for your project.

Choosing the right type of PVC for your project:
Choosing the right type of PVC for your project is essential to ensure optimal performance and durability. Consider the specific requirements of your project, such as the desired level of rigidity or flexibility, the operating temperatures, and the exposure to chemicals or harsh environments. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting the appropriate type of PVC:
- Rigidity or flexibility: Determine whether your project requires a rigid PVC, such as uPVC, or a flexible PVC, such as pPVC. Rigid PVC is suitable for applications that require strength and structural integrity, while flexible PVC is ideal for applications that require easy bending and manipulation.
- Heat resistance: If your project involves high temperatures, consider using CPVC, as it offers improved heat resistance compared to standard PVC. CPVC is commonly used in hot water supply systems and fire protection systems, where the higher temperatures necessitate a more heat-resistant material.
- Chemical resistance: Evaluate the level of chemical exposure in your project and choose a PVC type that offers the required chemical resistance. Rigid PVC, flexible PVC, and CPVC all offer good chemical resistance, but the specific chemical resistance properties may vary. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure compatibility with the chemicals involved.
- Environmental conditions: Consider the environmental conditions that your project will be exposed to, such as moisture, UV radiation, and harsh weather conditions. Foam PVC, with its resistance to moisture and weathering, is commonly used in outdoor applications, while rigid PVC and flexible PVC also offer good resistance to these conditions.
By considering these factors and understanding the unique characteristics of each type of PVC, you can select the most suitable material for your specific project. Consult with PVC manufacturers or suppliers for further guidance and recommendations based on your project requirements.
Common misconceptions about PVC
Despite its widespread use and versatility, PVC has been the subject of various misconceptions and concerns. It is important to address these misconceptions and provide accurate information about PVC. Here are some common misconceptions about PVC:
- PVC is harmful to the environment: While it is true that PVC production involves the use of certain chemicals, such as chlorine, it is important to note that PVC can be recycled and reused. PVC recycling programs exist in many countries, allowing for the recovery of PVC materials and reducing the environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in PVC production techniques have led to the development of more sustainable and eco-friendly PVC alternatives.
- PVC releases toxic substances: PVC is a stable material that does not release toxic substances under normal conditions of use. However, it is important to handle PVC products properly and follow safety guidelines, such as avoiding burning PVC or using it in high-temperature applications where it may release toxic fumes. By using PVC products responsibly and following safety precautions, the potential risks associated with PVC can be minimized.
- PVC is not durable: PVC, especially rigid PVC, is known for its durability and long-lasting performance. It is resistant to corrosion, weathering, and chemicals, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Additionally, advancements in PVC manufacturing have led to the development of additives and modifiers that further enhance the durability and performance of PVC materials.
PVC is only suitable for low-quality products:
PVC is used in a wide range of industries and applications, including construction, healthcare, packaging, and automotive. It is a versatile material that offers a combination of properties, such as rigidity, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for both high-quality and low-quality products. The quality of PVC products ultimately depends on the manufacturing processes and the specific requirements of the application.
By addressing these misconceptions and providing accurate information about PVC, it is possible to promote a better understanding of this versatile material and its applications. PVC, when used responsibly and in accordance with safety guidelines, can provide numerous benefits and contribute to sustainable and innovative solutions.
FAQS for What are the 4 types of PVC?
Q1: What are the four types of PVC?
A1: The four main types of PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) are Rigid PVC, Flexible PVC, Chlorinated PVC (CPVC), and Polyvinyl Chloride-U (PVC-U). Each type has distinct characteristics and is used in different applications.
Q2: What is Rigid PVC, and where is it used?
A2: Rigid PVC, also known as unplasticized PVC or PVC-U, is a stiff, non-flexible form of PVC. It is commonly used in applications such as pipes, fittings, window frames, and construction materials due to its durability and chemical resistance.
Q3: What is Flexible PVC, and where is it used?
A3: Flexible PVC, often referred to as PVC-P, is a softer, more pliable form of PVC. It is used in products like inflatable structures, hoses, cable insulation, and medical devices due to its flexibility and ease of processing.
Conclusion
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a versatile material that finds applications in various industries and products. Understanding the different types of PVC is important in determining the most suitable material for your specific application. Rigid PVC, or uPVC, offers rigidity and strength, making it suitable for building and construction projects. Flexible PVC, or pPVC, provides enhanced flexibility and is commonly used in soft products like cables, inflatable toys, and medical devices. Chlorinated PVC, or CPVC, offers improved heat and flame resistance compared to standard PVC and is commonly used in plumbing systems and fire sprinkler systems. Foam PVC, or expanded PVC, is a lightweight and versatile material used in the signage industry and construction industry.
By considering the specific characteristics and applications of each type of PVC, you can choose the right material for your project. Whether you need rigidity, flexibility, heat resistance, or chemical resistance, there is a type of PVC that can meet your requirements. Addressing common misconceptions about PVC is also important in promoting a better understanding of this versatile material and its benefits.
Next time you encounter PVC in your daily life or in a project, remember the four types of PVC and their unique characteristics. By choosing the right type of PVC, you can ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety for your application. PVC truly is a material that offers endless possibilities and solutions for a wide range of industries and products.