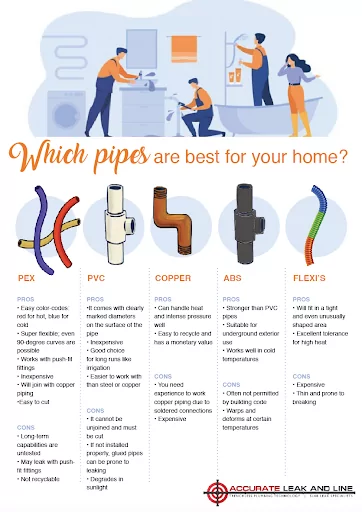
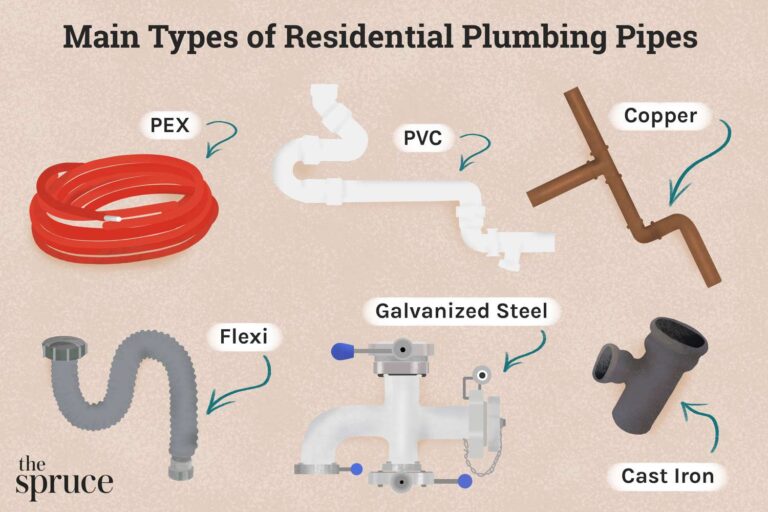
What Is PVC In Soil?
PVC in soil is a type of plastic that is commonly used in construction and agricultural applications. PVC stands for polyvinyl chloride, which is a type of thermoplastic material that is strong, durable, and resistant to corrosion. In soil, PVC is often used to line trenches and channels, to prevent water infiltration, to create drainage systems, and to protect against soil erosion. PVC can also be used to construct septic systems, water supply lines, and irrigation systems. It is an effective and affordable material that can help to improve soil health and increase crop yields.
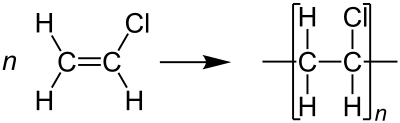
What is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a synthetic plastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is a thermoplastic polymer that is durable, versatile, and inexpensive, making it an ideal material for many applications. PVC is a common material used in soil stabilization projects, such as for infrastructure, roadways, and other construction projects. PVC is also used in agricultural projects, such as for crop protection and drainage systems. It is a popular choice for soil stabilization due to its strength, durability, and chemical resistance.
PVC can provide soil stabilization by increasing the strength and stability of the soil, and by preventing the movement of soil particles. It can also help to prevent erosion and provide greater water-holding capacity. In addition, PVC can provide a weather-resistant barrier to protect plants and crops from frost and other environmental conditions. PVC is a relatively inexpensive material and is easy to install, making it a cost-effective choice for soil stabilization projects.
The use of PVC in soil stabilization projects can help to reduce the impact of soil erosion and improve the overall soil structure. It can also help to increase crop yields, reduce labor costs, and improve the overall environment. PVC is an important material for soil stabilization projects, and its use can help to ensure the success of these projects.
Role of PVC in Soil
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a type of plastic commonly used for various purposes. In the field of soil science, it has become increasingly important due to its ability to improve soil structure and water retention. PVC is used to stabilize and reduce erosion, improve drainage, and increase the fertility of soil. It also helps to reduce the compaction of soil and to improve the infiltration of water and air. PVC is also used to improve the strength of soil and to reduce the risk of flooding. PVC is an effective soil conditioner that can be used to improve soil fertility, water retention, and drainage. It also helps to reduce the compaction of soil and to increase the infiltration of water and air. Additionally, PVC can be used to reduce the risk of flooding and to enhance the strength of soil. By using PVC in soil, farmers can create a more productive and sustainable soil environment for their crops.
Benefits of PVC in Soil
Soil is a key element in the success of any garden or landscape project. PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a material that can be used to improve soil structure and fertility. It can help plants to thrive and can even extend the life of your plants. PVC can also help to keep soil from becoming compacted and can improve drainage in areas with poor drainage. It’s a great material for any garden or landscape project, as it’s strong, lightweight, and cost-effective. PVC can also be beneficial to the environment, as it can help to reduce water runoff and erosion.
PVC in soil can also help to reduce soil-borne diseases and pests. It can be used to create a barrier between the soil and plant roots, keeping out disease-causing organisms. Additionally, PVC can help to improve the fertility of the soil, as it can help to retain water and fertilizer. This can be especially useful for gardens in dryer climates. PVC can also be used to create a barrier between the soil and plant roots, reducing the risk of root rot and other diseases.
Overall, PVC is an excellent material to use in soil for many different reasons. It can help to improve soil structure, increase fertility, reduce water runoff, and protect from soil-borne diseases and pests. PVC is also strong, lightweight, and cost-effective, making it a great choice for any garden or landscape project.
Disadvantages of PVC in Soil
Soil is an integral part of the planet’s ecosystem and maintaining its integrity is essential to the environment’s health. Unfortunately, due to human activities, soil can be contaminated with substances that can be detrimental to the environment. One such substance is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). PVC is a type of synthetic plastic that is commonly found in pipes, wires, and other products. It is also found in soil, but its presence there can be dangerous.
PVC is toxic to plants and animals, and it has been linked to a variety of health problems in humans. PVC can also leach heavy metals and other contaminants from the soil into groundwater, which can be dangerous to drink. PVC can also bind to certain organic compounds, making them unavailable for use by plants. This can lead to decreased crop yields and soil erosion.
In addition to its environmental impact, PVC can also be expensive to remove from contaminated soil. Since the plastic is so durable, it can take a long time and specialized equipment to remove it. Even after removal, the soil may still be contaminated with other substances that can be difficult to remove.
Overall, PVC can have serious environmental and economic consequences when found in soil. It is important to avoid contaminating soil with PVC and take steps to remove it when present.
Common Uses of PVC in Soil
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a versatile material with a wide range of uses in soil. From agricultural applications to environmental protection, this plastic material is often used to modify soil properties, improve drainage, and protect against potential hazards. It can also be used to transport and store water, fertilizers, pesticides, and other substances. PVC is extremely durable and can withstand extreme temperatures, making it an ideal choice for a variety of soil-related applications. In addition, it does not corrode, rust, or rot, meaning it is a sustainable and cost-effective option for soil-related projects. The flexibility of PVC makes it easy to shape and form into whatever shape is needed, making it a great choice for projects that require a custom or unique design. PVC is also relatively lightweight, making it easy to transport and install.
From agricultural irrigation systems to landfill liners, PVC is an ideal material for a variety of soil-related projects. Its flexibility and durability make it a great choice for projects where soil needs to be modified or protected from potential hazards. PVC also has a wide range of uses in soil-related projects, from creating barriers to aiding in crop growth. With its many benefits, PVC is a great option for any project that requires a durable and cost-effective material.
Alternatives to PVC in Soil
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a popular material used in many soil applications, however, there are a number of alternatives that can be used in its place. Alternatives to PVC in soil include polypropylene, polyethylene, and biodegradable polymers. Each of these materials has its own advantages and disadvantages, but they all offer a viable option if you are looking for an alternative to PVC.
Polypropylene is a strong, lightweight plastic that is resistant to corrosion and chemicals, making it a popular choice for soil applications. It is also UV-stable, meaning it can withstand exposure to the sun’s rays. However, it is not as durable as PVC and is more expensive.
Polyethylene is a versatile plastic that is often used in soil applications due to its low cost and flexibility. It is also resistant to water, chemicals, and temperature changes. However, it is not as strong as PVC and can be prone to cracking.
Biodegradable polymers are an environmentally friendly alternative to PVC. They break down over time and are not harmful to the environment. They are also lightweight and strong, making them an attractive option for many soil applications. However, they are more expensive than other alternatives and can be more difficult to work with.
No matter which material you choose, it is important to consider your specific needs and the environment in which the soil is being used. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to do your research and make sure you are choosing the right material for the job.
FAQs About the What Is PVC In Soil?
Q1: What is PVC in soil?
A1: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a type of plastic material commonly found in soil. It is used in a variety of products such as pipes, siding, and electrical insulation.
Q2: Is PVC harmful to soil?
A2: PVC is not necessarily harmful to soil, but it can be a pollutant if it is not disposed of properly. PVC can leach chemicals into the soil, which can be toxic to plants and animals.
Q3: How do I remove PVC from my soil?
A3: PVC can be difficult to remove from soil, so it is important to use the correct methods. The most effective way to remove PVC from soil is to aerate the soil, which allows the PVC particles to be absorbed and broken down. Alternatively, you can use a vacuum cleaner to remove the PVC particles.
Conclusion
PVC in soil can be a major issue for the environment due to its toxicity. PVC can leach toxic chemicals into the soil, water, and air, contaminating the environment and posing a potential health hazard. To reduce the risk of PVC in soil, it is important to reduce the use of PVC materials and dispose of them properly in order to reduce the risk of contamination.