What Is Soil Porosity?
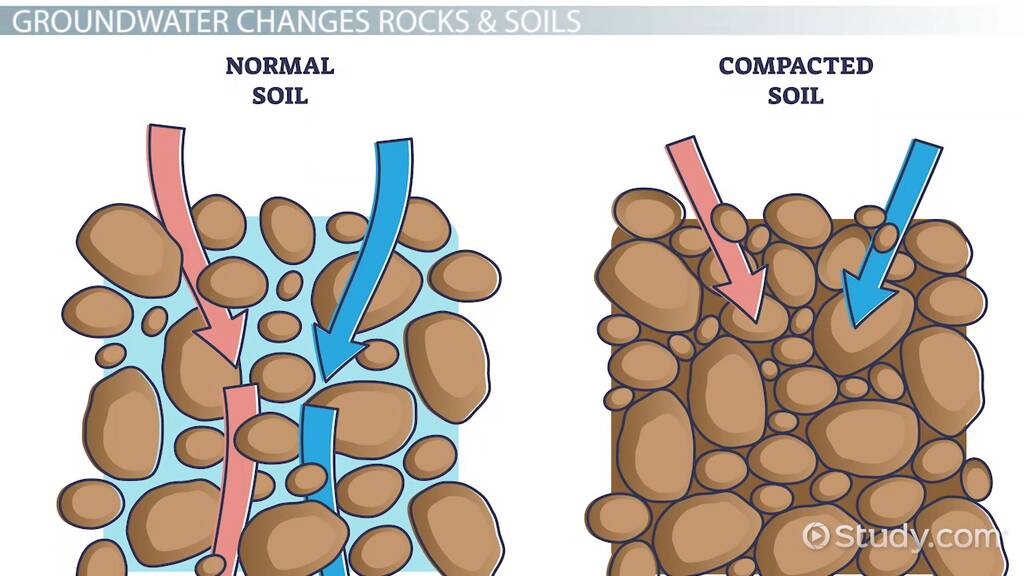
Soil porosity is the measure of the amount of space in soil. It is a measure of the amount of pore spaces between the soil particles. Soil porosity is an important factor when considering water infiltration, drainage, and oxygen availability to soil organisms. It is also important for seedling emergence and root growth. Porosity affects the amount of water and air a soil can hold, its nutrient supply, and its ability to support vegetation.
Definition of Soil Porosity
Soil porosity is the measure of how much pore space exists within a soil sample. It is a crucial component of soil structure and is affected by a variety of factors such as soil texture, organic matter content, and compaction. In essence, it serves as a measure of how much air and water are held in the soil, and therefore how well the soil can support plant growth. It is important to understand soil porosity in order to effectively manage soil health and fertility.
Soil porosity is typically measured in terms of its total porosity, which is the percentage of the total soil volume that consists of pore space. This percentage can range from a few percent in very compacted soils to more than 50 percent in very loose soils. Soil porosity can also be measured in terms of its macroporosity, which is the percentage of the total soil volume that consists of large pore spaces that are large enough for water and air to move through.
Soil porosity is an important indicator of soil health, as it directly affects the availability of water and air to plants. Porosity also influences the movement of water and nutrients through the soil, and can affect soil temperature and microbial activity. As such, understanding soil porosity is an important part of soil management and can help ensure soil fertility and sustainability.
Factors that Affect Soil Porosity
Soil porosity is a measure of the air and water that can move through soil. It is an important factor when evaluating soil quality and fertility. Factors such as texture, structure, and organic matter content can all impact soil porosity. Understanding how these different factors affect soil porosity can help farmers and gardeners make informed decisions about how to best manage their soil.
Texture is the size and shape of individual soil particles and can affect how much air and water can move through soil. Soils with larger particles typically have more air and water movement than those with smaller particles. Soils with a large sand content tend to have more air movement than soils with a large clay content.
Structure is the arrangement of soil particles. Soils with a well-developed structure tend to have more air movement than soils with a poorly developed structure. Soils with a good structure also tend to be better at draining water than those with a poorly developed structure.
Organic matter is the decaying plant material that is found in soil. It can act like a sponge, absorbing and retaining water and nutrients. Organic matter also increases the porosity of soil, allowing more air and water to move through it.
Understanding how these different factors affect soil porosity can help farmers and gardeners make informed decisions about how to best manage their soil. By adding organic matter, improving soil structure, and adjusting the texture, they can improve the porosity of their soil and ensure that the air and water are able to move freely through it.
Benefits of Soil Porosity
Soil porosity is an important factor in the health of a garden. It determines the amount of water and air that can be held in the soil, which affects the health of plants. Porosity is the measure of the volume of soil pores or the empty space between soil particles. It is important to understand the benefits of soil porosity in order to create a healthy environment for plants.
Soil porosity helps regulate the temperature of the soil. Since the soil particles are not packed together tightly, the air and water can move freely through the soil and help to keep the soil temperature consistent. This is beneficial for plants that prefer a consistent environment, such as vegetables.
Soil porosity also helps to reduce compaction and improve drainage. When soil particles are not tightly packed together, the soil can hold more water without becoming saturated. This prevents the soil from becoming too compact, allowing the roots of plants to access the nutrients they need to grow. Additionally, improved drainage helps to keep the soil from becoming water-logged.
Soil porosity also improves the ability of roots to penetrate the soil. When the soil particles are not tightly packed together, the roots of plants can easily make their way through the soil to find the nutrients they need. This helps to promote healthy root development and allows plants to reach their full potential.
Overall, soil porosity is an important factor for the health of a garden. It helps to regulate the temperature of the soil, reduce compaction, improve drainage, and promote healthy root growth. Understanding the benefits of soil porosity can help gardeners create an optimal environment for their plants to thrive.

Methods for Measuring Soil Porosity
Soil porosity is an important physical property of soil for agricultural, environmental and engineering purposes. It is a measure of the amount of air, water, and other fluids that can be held by a soil. Porosity is determined by the size, shape, and arrangement of the soil particles. There are several methods for measuring soil porosity, each with different advantages and drawbacks. This article will discuss the various methods for measuring soil porosity, including the core-sampling method, the porosity index method, the filter paper method, and the air-filled porosity method.
The core-sampling method is used to measure the total porosity of the soil, including both the macropores and the micropores. It involves taking a core sample from the soil, and then measuring the total volume of the sample. The porosity index method is a laboratory-based technique used to measure the total porosity of the soil. It involves measuring the weight and volume of the soil sample, and then calculating the porosity of the sample. The filter paper method is a simple and inexpensive method used to measure the pore size distribution of the soil. It involves placing a filter paper on the soil sample and measuring the amount of water that passes through the paper. The air-filled porosity method is a laboratory-based technique used to measure the volume of air-filled pores in the soil. It involves measuring the pressure difference between a sample of soil and a reference pressure.
By using one or more of these methods, the porosity of soil can be accurately measured. This is important for understanding the physical and chemical properties of the soil, which are essential for a wide range of applications, including agricultural, engineering, and environmental purposes.
Ways to Improve Soil Porosity
Soil porosity is the capacity of soil to hold air and water within its pores. It has a direct impact on the health and productivity of plants, aiding in the absorption of water and nutrients. Improving soil porosity allows for better water retention, aeration, and drainage, resulting in healthier plants. Fortunately, there are several ways to improve soil porosity.
Aeration is one of the most effective methods for improving soil porosity. Aeration loosens the soil and allows for better airflow and water absorption. This can be done manually by using a garden fork, or mechanically with a motorized aerator.
Adding organic matter to the soil is another way to improve porosity. Compost, manure, and other organic materials help to break down clay particles in the soil and create a looser structure. This increases the amount of air pockets in the soil, allowing for better water retention and drainage.
Cover crops are another great tool for improving soil porosity. Cover crops create a living mulch that helps to break up soil particles and improve air circulation. The cover crops also help to prevent erosion and suppress weeds.
Finally, adding gypsum is a great way to improve soil porosity. Gypsum helps to reduce soil compaction, allowing for better aeration and drainage. Gypsum also helps to break up clay particles, improving water absorption.
Improving soil porosity is essential for healthy and productive plants. Aeration, adding organic matter, planting cover crops, and adding gypsum are all effective methods for improving soil porosity and creating the conditions for a healthy and productive garden.
Common Problems Related to Low Soil Porosity
Soil porosity is an important factor in the health of soil and plants. It is a measure of the air and water in the soil, as well as the amount of space available for roots to grow. Low soil porosity can lead to a variety of problems, such as poor drainage, a lack of oxygen, and compaction. Poor drainage can lead to standing water and anaerobic conditions, resulting in root rot and other plant diseases. In addition, low oxygen levels can slow down the development of beneficial soil organisms and restrict the growth of plant roots. Compaction can also impede the movement of water and air through the soil and limit the ability of plants to take up nutrients.
The best way to address low soil porosity is to prevent it in the first place. Adding organic matter to the soil can help improve its structure and increase its porosity. For existing problems, regular aeration and tilling can help improve the soil structure. Additionally, mulching and adding compost can also help create a more porous soil structure, as well as provide additional nutrients to the soil. Taking care of the soil is an important part of ensuring healthy plants and a healthy environment. By understanding soil porosity and the potential problems it can cause, we can take steps to ensure that the soil is in its best condition.
FAQs About the What Is Soil Porosity?
1. What is soil porosity?
Answer: Soil porosity is the voids or spaces created between soil particles. It determines the amount of water and air that can be stored in the soil.
2. How does soil porosity affect plant growth?
Answer: Soil porosity affects the amount of water and oxygen available to plants, as well as the amount of nutrients and minerals that can be taken up by the roots. A higher soil porosity means more air and water can be held in the soil, resulting in improved plant growth.
3. What factors affect soil porosity?
Answer: Soil porosity is affected by the type of soil particles, their size and shape, and the amount of organic matter present in the soil. Other factors such as soil compaction, erosion, and tillage can also influence soil porosity.
Conclusion
Soil porosity is an important concept that is essential to understanding how water and air interact with soil. Soil porosity is the measure of the voids in the soil that contain air and water. It is an important characteristic that affects the water-holding capacity and the availability of water and air to the roots of plants. As such, it is important for farmers and gardeners to understand how soil porosity affects their crops.