Is PVC Biodegradable?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a type of plastic used for a wide range of applications, from pipes and flooring to window frames and furnishings. While it is a durable material, it is not biodegradable, meaning it does not break down naturally in the environment. Instead, it persists for hundreds of years, posing a threat to wildlife and the environment. As such, it is important to be mindful of the amount of PVC being used and disposed of, and to look for more sustainable alternatives whenever possible.
What is PVC?
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a type of plastic used for a variety of purposes in everyday life. It is a durable, versatile, and cost-effective material that finds use in construction, furniture, medical equipment, and many other products. PVC is made from chlorine and ethylene, two natural gas by-products, and is recyclable, although it is not biodegradable. This means that while it can be reused, it will remain in the environment indefinitely when discarded, potentially causing environmental harm. PVC is also potentially hazardous to humans, as it can release toxic chemicals when burned. As a result, it is important to dispose of PVC responsibly and to take into account its environmental impact before using it.
Potential Environmental Impact of PVC
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is one of the most widely used synthetic materials in the world. It is used for a variety of applications, ranging from packaging and construction to medical devices and toys. But as with many other synthetics, PVC is non-biodegradable, meaning it will not break down naturally over time. This raises significant environmental concerns about the long-term impact of our ever-growing reliance on PVC.
The most significant environmental concern is the release of hazardous chemicals such as phthalates, a common plasticizing agent. Phthalates can leach into the environment through PVC products, and have been linked to a range of health issues such as endocrine disruption, reproductive toxicity, and cancer. Additionally, PVC production often requires the use of toxic chemicals like chlorine and heavy metals such as cadmium, which can damage ecosystems and contaminate sources of drinking water.
The other major environmental concern is the energy required to produce PVC. Manufacturing PVC requires large amounts of energy, and the production process releases greenhouse gases, further contributing to climate change.
In conclusion, PVC is a widely used synthetic material that has significant environmental implications. The chemicals used in its production and the energy required to manufacture it can be damaging to the environment and human health. To minimize the environmental impact of PVC, it is important to use it responsibly and consider more sustainable alternatives.
Does PVC Biodegrade?
PVC or polyvinyl chloride is a type of plastic widely used in a variety of products from construction materials to medical devices to toys. But what happens to PVC when it’s discarded? Is it biodegradable? The answer is no, it is not biodegradable. That means it will stay in the environment for hundreds of years, and it will never decompose completely.
PVC does not break down in water, air or sunlight, and it does not contain the necessary enzymes or bacteria needed to decompose it either. It may eventually fragment into smaller pieces, but it will never decompose into its original components. This means that it can’t be used as a source of nutrients or energy for other organisms, and it’s not capable of being recycled.
While PVC is not biodegradable, it can be recycled or reused in some cases. However, this is not a complete solution to the problem of disposing of PVC waste, as not all types of PVC can be recycled easily. Additionally, the energy and resources required to recycle it are considerable.
The best way to reduce the environmental impact of PVC is to reduce consumption and reuse the material when possible. That said, there are some steps being taken to make PVC biodegradable, such as using additives that allow it to break down in certain conditions. However, this technology is not yet widely available.
Effectiveness of PVC Biodegradation
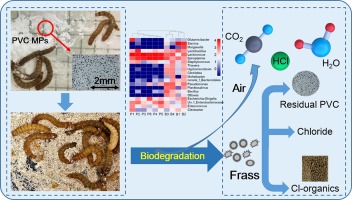
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a popular material used in construction, electrical wires, and packaging applications. As with other plastics, it is generally considered to be non-biodegradable, meaning that it will not break down in the environment over time. However, recent research suggests that PVC may be more biodegradable than previously thought. This article examines the potential for PVC biodegradation and looks at the effectiveness of various methods of breaking down PVC.
Studies have shown that some microorganisms are capable of breaking down PVC in the presence of certain conditions. These include the presence of oxygen, adequate moisture, and certain enzymes. The process is relatively slow and may take several months to years to complete. In addition, the presence of certain contaminants can inhibit the process.
Researchers have also investigated methods of accelerating the biodegradation of PVC. One approach is the use of microbes that are engineered to break down plastics more quickly. Another approach is the use of chemical agents that can help to break down the polymers in PVC. However, these methods are still in the early stages of development and are not yet widely available.
Ultimately, it appears that PVC can be biodegraded, but the process is slow and not yet widely available. It is important to remember that biodegradation is not a solution to the problem of plastic waste, as the broken-down components can still cause environmental damage. Therefore, it is important to continue to focus on reducing plastic consumption and improving waste management systems.
Alternatives to PVC
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a popular material used in a variety of applications, but its non-biodegradable nature has caused concern for its environmental impact. There are several sustainable alternatives to PVC, each of which offers its own benefits and drawbacks.
One such alternative is recycled plastic, which can be reused for various products without the need for additional processing. This helps to reduce waste and conserve energy, while still providing a durable and cost-effective material.
Bioplastics are another alternative, with the majority being made from renewable resources such as plants. This makes them biodegradable, which is great for the environment. However, bioplastics are not always as durable as PVC and may require more energy to produce.
Finally, there are other materials such as bamboo, linen, and cotton that are renewable and biodegradable. These materials can provide an eco-friendly alternative to PVC but may not be suitable for certain applications due to their lack of durability.
Ultimately, the choice of material depends on the specific application and the environmental impact that is desired. PVC is still a popular choice for many applications, but if biodegradability is a concern then there are several alternatives that should be considered. By doing so, it is possible to reduce waste and create a more sustainable future.
FAQs About the Is PVC Biodegradable?
1. Is PVC biodegradable?
Answer: No, PVC is not biodegradable. It is a type of plastic that is resistant to most forms of degradation and will not break down in the environment.
2. What is the best way to dispose of PVC?
Answer: The best way to dispose of PVC is to take it to a recycling center that specializes in plastic recycling. This will ensure that the PVC is reused rather than sent to a landfill.
3. Can PVC be composted?
Answer: PVC cannot be composted as it is not biodegradable. Composting is a method of breaking down organic materials that are biodegradable.
Conclusion
Based on the available research, it is clear that PVC is not biodegradable and has a long-term environmental impact. While there are some methods of degradation that can be used to reduce the amount of PVC in the environment, these methods are not yet widely used. As a result, it is important to consider the environmental impact of using PVC before making the decision to use it in any application.